We all know the axiom ‘know thy enemy’ – and this is above all germane to DDoS attacks.
Cybercriminals and their tactics are always evolving, becoming more dangerous and harder to detect by the day.
Unlike a Denial of Service (DoS) attack, in which a single Internet-connected device causes disruption and destruction. DDoS attacks are launched from numerous compromised devices, often dispersed globally in what is referred to as a botnet and controlled remotely by the botnet herder using a covert channel, such as Internet Relay Chat (IRC).
Some of the larger botnets whose name comes from the malware used to infect them are estimated to be in the millions of bots including Zeus or Zbot, Conficker, and BredoLab or Oficla to name a few.
It is estimated that upwards of 3000+ websites fall victim to DDoS attacks daily. Regardless if the websites are back up and running the same day, damages to both revenue and customer and/or client trust can follow organizations for years.
The primary purpose of the DDoS is to overload network layers with a substantial amount of outwardly legitimate traffic. Ultimately the traffic consumes a disproportionate amount of bandwidth within and/or outside of the network and pushes network operations to become excruciatingly sluggish or basically nonfunctional.
Adding to the confusion, botnet servers can be controlled either by a single botnet herder or by multiple herders. Ultimately, at any given DDoS attack there can be multiple origins and multiple controllers making it much more complicated to mitigate than attacks originating from a single source.
The aggressiveness of DDoS attacks was illustrated last year by the Mirai Botnet in which the attacks besieged several systems using corrupted Internet of Things (IoT) devices. 
The expectation of IoT is upwards of 25 Billion televisions, refrigerators, watches, thermostats, and other connected devices by 2020; most with minimum to zero security in order to prevent malware infections. Resulting in an unknown amount of IoT devices ending up as mindless bots caught up in a criminal botnet.
To make matters worse, roughly 40 percent of malicious bots are able to emulate human behavior. Not only do the malicious bots deceptively present themselves to websites as legitimate bots, but they can also persistently change identities.
The infrastructure which enables these attacks is also increasing 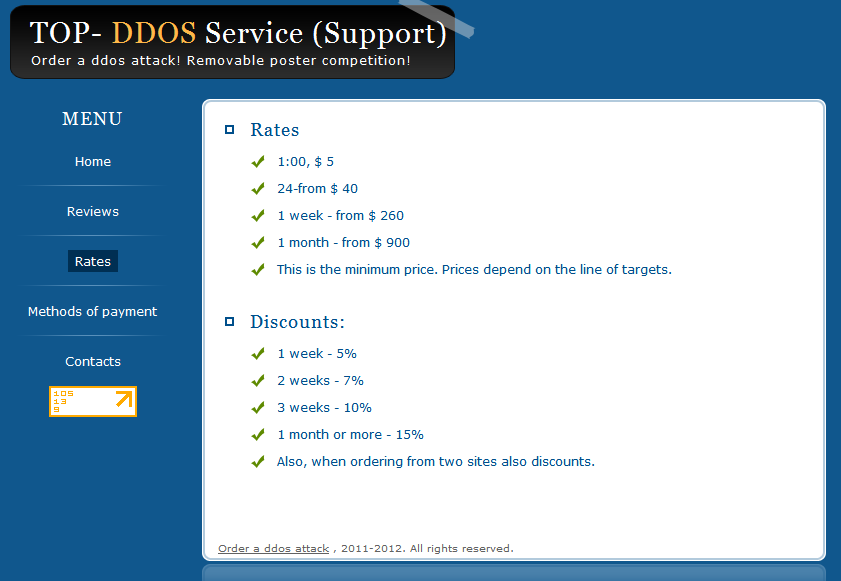 dramatically. Anyone with mal intentions can easily purchase on-demand botnet services for DDoS attacks.
dramatically. Anyone with mal intentions can easily purchase on-demand botnet services for DDoS attacks.
They are readily available from multitudes of online sources; for as little as $5 an hour to $40 per day; Cloaked behind the definition of Booters or stressers services.
They are also referred to as ddoser, ip stresser, ddos tools and ddos programs. No matter the name, they all provide the same service- providing paying customers with on-demand DDoS attack capabilities, at will.
Below find some of the more well-known Booters and Stressers which are easily accessed on the Internet.
NetworkStresser.com
120GB/s of combined power. Takes down everything. Working Skype resolver. Active support. Multiple payment options.
Betabooter.com
100GB/seconds. Easy to use. API. Insane Power. Accepts Paypal.
Critical-Boot.com
Good Power. Easy to use source. PayPal/Credit cards and 15% off Bitcoin. Build Your Plan.
There are three standard types of DDoS attacks including Volumetric, Application, and Protocol attacks.
Volumetric Attacks utilize massive amounts of traffic inundating the bandwidth of the host.
Volumetric attacks are generated by employing amplification techniques which primarily elicit server responses that are disproportionate to the original packet request sent; ultimately completely blocking access to a website or service. The extent of the attack is measured in either bits or packets per second. Domain Name System Servers (DNS) Amplification being a well known volumetric attack.
DNS amplification is an asymmetrical attack in which the  criminal exploits vulnerabilities in DNS servers, i.e., ‘The Internet’s Backbone’ by manipulating publically-accessible domain name system servers by querying the DNS with spoofed or ‘faked’ target IP’s and making them flood a server with large quantities of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets.
criminal exploits vulnerabilities in DNS servers, i.e., ‘The Internet’s Backbone’ by manipulating publically-accessible domain name system servers by querying the DNS with spoofed or ‘faked’ target IP’s and making them flood a server with large quantities of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets.
This results in small queries being turned into massive payloads that can ultimately be used to bring down even the most robust server(s).
Moreover, DNS amplification attacks often relay the exploited DNS requests through one or more botnets, radically increasing the volume of traffic and making it that harder to track the attacker(s) identity(s).
 Application Attacks exploit a weakness in the Layer 7 or as the name suggests the application layer.
Application Attacks exploit a weakness in the Layer 7 or as the name suggests the application layer.
The cyber community, in general, agrees that application attacks are both the most sophisticated and the most challenging to identify and/or mitigate.
Application attacks begin with making a connection with the host then it exhausts the  host’s resources by controlling processes and transactions. DNS Flood attacks are the most well known.
host’s resources by controlling processes and transactions. DNS Flood attacks are the most well known.
DNS floods are a symmetrical attack that endeavors to exhaust server-side assets like memory or CPU, with an inundation of UDP requests, generated by malicious scripts running on multiple botnet machines. The criminals will often target one or more DNS servers belonging to a specified zone, with the goal of obstructing and overwhelming the resolution of resource records of that zone and its subzones.
Protocol attacks specifically exploit weaknesses in the Layer 3 and Layer 4 protocol stack by consuming all the processing capacity of the intermediate critical resources like a firewall causing service disruption; With the most notorious attack being the Ping of Death.
A ‘ping’ is part of the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) which is a networking utility that determines whether or not a host is reachable. The ICMP request packet is sent to the host, which the host then responds with an ‘echo’ reply. The size of an accurately formed ICMP request packet should be no larger than 65,535 bytes; anything larger is in violation of the Internet Protocol.
Criminals, in turn, send malformed packets in fragments as fast as possible in which the host attempts to assemble using up bandwidth. This leads to a packet size which violates the internet protocol of 65,535 bytes causing a buffer overflow, and eventually causing the host to crash and become unavailable for legitimate users. This is a Ping of Death DDoS attack.
DDoS scripts are written most often in Python, PHP, or Pearl and refers to malicious software that enables the execution of DDoS attacks.Each script can diverge in severity, ease of use and impact and attacks at the application layer.
Some of the DDoS scripts available for free on the internet (too many to list) include
LOIC (Low Orbit In Canon)
LOIC was made famous by the hacker group Anonymous. It is easy to use especially for beginners, because of its easy-to-use GUI; all you need is the URL of the IP address of the server. LOIC performs the DOS by sending UDP, TCP, or HTTP requests to the victim server.
XOIC
XOIC comes with an easy-to-use GUI, so all levels can easily use it to perform attacks on servers and websites anonymously and secretly. All that is required is an IP address.
XOIC has three methods including, Test mode; Attack mode; Attack mode with a TCP/HTTP/UDP/ICMP Message.
TORsHammer
Tors Hammer is written in Python, and it is a slow post tool* that can be run through the TOR network** and can kill most unprotected web servers running Apache and IIS by means of a single occurrence.
HOIC (High Orbit in Cannon)
HOIC is written in BASIC and is an open source network stresser that can attack as many as 256 URLs at any one time.
Slowloris
Slowloris is written in Python and operates at the application layer. It opens as many connections to the web server as it can, and holds them open as long as possible by sending partial requests, and periodically adding them to keep the connection alive but never completing and denying connection attempts from legitimate users.
DDoS toolkits are software packages that require greater resources and generally more in-depth knowledge of scripting and systems and attacks the network layer. They infect computers and other Internet-connected devices (IoT) with malware in order to build a botnet.
The malicious bot landscape continues to evolve. Considering that more than 60 percent of the Internet traffic is generated by bots of which upwards of 30 percent is represented by malicious bots which present a force to be reckoned with when talking about internet security.
DDoS attacks can be unassuming or sophisticated, regardless, they are always  dangerous, calculated and profit-driven with DDoS ransom being one of the nastiest elements.
dangerous, calculated and profit-driven with DDoS ransom being one of the nastiest elements.
Extortionists will demonstrate their capabilities by acting out an attack such as shutting down a website, followed by a threatening e-mail requesting a monetary sum usually in Bitcoin to be paid within a time-period. ‘Pay the ransom or face greater attacks.’
The extortionists will continue broadening their scope and diversifying their targets to include more diverse industry sectors and larger organizations and even larger payoffs.
Below find a few strategies which can make your network less vulnerable to attackers, remembering, there is No 100 Percent Solution to prevent cyberattacks. Continuous learning and continuous experimentation are critical.
- Limit the number of new connections. Set parameters for the number of new connections during specific periods of time by a single user or by the network. Doing this simple strategy will make it that much harder for a criminal to overload systems.
- Bandwidth Shaping. If configured correctly, bandwidth shaping can be an easy to apply policy against DDoS attackers.
- Network Segmentation. By dividing your network into segments into public and internal sections, each protected by a firewall, this tactic can support your internal network when there is a DDoS attack against your public-facing systems.
CyberSecurity is a shared responsibility. Stop. Think. Connect.
 As the world becomes ever more data-driven, data breaches become more intense and more frequent with data records exposed on an almost daily basis with potentially devastating consequences. Everyone is at risk. Today’s organizations have to shift their focus toward technologies that inherently protect and secure data. Enter the Blockchain technology.
As the world becomes ever more data-driven, data breaches become more intense and more frequent with data records exposed on an almost daily basis with potentially devastating consequences. Everyone is at risk. Today’s organizations have to shift their focus toward technologies that inherently protect and secure data. Enter the Blockchain technology.

 The DNS infrastructure is the backbone of the internet, and it is irreplaceable. Fundamentally, DNS serves as the internet’s phone book. To simplify it even further:
The DNS infrastructure is the backbone of the internet, and it is irreplaceable. Fundamentally, DNS serves as the internet’s phone book. To simplify it even further: 
 simply rent, lease or purchase an ‘
simply rent, lease or purchase an ‘ highly sophisticated cyber criminals with substantial financial backing.
highly sophisticated cyber criminals with substantial financial backing.
 through ‘authentication,’ i.e., ‘the extension of trust’ based on a form of furnished proof of identity, that proof is more often than not a password.
through ‘authentication,’ i.e., ‘the extension of trust’ based on a form of furnished proof of identity, that proof is more often than not a password.
 data as the result of not backing up their data, and
data as the result of not backing up their data, and 

 trying to break into our systems and stealing our data. However, what is often overlooked is that one of the biggest threats to our organizations is already lurking inside.
trying to break into our systems and stealing our data. However, what is often overlooked is that one of the biggest threats to our organizations is already lurking inside. Then there are the malicious insiders who pose the greatest threats, in part because it is incredibly easy for employees who have access to the organization’s network to misappropriate data, use data extrusion or destroy/alter the data.
Then there are the malicious insiders who pose the greatest threats, in part because it is incredibly easy for employees who have access to the organization’s network to misappropriate data, use data extrusion or destroy/alter the data. criminals stand to haul in huge financial paydays if they can collect that data. Moreover, evidence suggests that cyber criminals have begun collecting this valuable data by recruiting employees and turning them into malicious insider threats. According to new research from IBM, the
criminals stand to haul in huge financial paydays if they can collect that data. Moreover, evidence suggests that cyber criminals have begun collecting this valuable data by recruiting employees and turning them into malicious insider threats. According to new research from IBM, the 
 criminals know this is an area of weakness and they target it, and more often than not, very successfully.
criminals know this is an area of weakness and they target it, and more often than not, very successfully. owned the servers and constructed malicious software (malware) from scratch.
owned the servers and constructed malicious software (malware) from scratch. Today, it is a distributed system where anyone with an agenda can simply rent, lease or purchase an ‘as a Service,’ services and ‘cash in’ on their crimes.
Today, it is a distributed system where anyone with an agenda can simply rent, lease or purchase an ‘as a Service,’ services and ‘cash in’ on their crimes. facilitation of cybercrimes, because of the anonymity under which groups are able to operate.
facilitation of cybercrimes, because of the anonymity under which groups are able to operate. advantages to the information technology industry but also greater opportunities for cybercriminals.
advantages to the information technology industry but also greater opportunities for cybercriminals. digital money that utilizes a decentralized, peer-to-peer (P2P) payment network thus making it harder to discover criminal activity.
digital money that utilizes a decentralized, peer-to-peer (P2P) payment network thus making it harder to discover criminal activity. second wallet is created, again, utilizing TOR, and moves the funds into the second wallet. Last but not least, a third wallet is created, and the funds are moved again, thus confusing the trail of transactions between the three wallets making attribution almost impossible.
second wallet is created, again, utilizing TOR, and moves the funds into the second wallet. Last but not least, a third wallet is created, and the funds are moved again, thus confusing the trail of transactions between the three wallets making attribution almost impossible. bitcoins which add a ‘proprietary obfuscation technology’ that breaks the link to the source of the funds and prevents any
bitcoins which add a ‘proprietary obfuscation technology’ that breaks the link to the source of the funds and prevents any 



 dramatically. Anyone with mal intentions can easily purchase on-demand botnet services for DDoS attacks.
dramatically. Anyone with mal intentions can easily purchase on-demand botnet services for DDoS attacks. criminal exploits vulnerabilities in DNS servers, i.e.,
criminal exploits vulnerabilities in DNS servers, i.e.,  Application Attacks exploit a weakness in the Layer 7 or as the name suggests the application layer.
Application Attacks exploit a weakness in the Layer 7 or as the name suggests the application layer. host’s resources by controlling processes and transactions. DNS Flood attacks are the most well known.
host’s resources by controlling processes and transactions. DNS Flood attacks are the most well known.
 dangerous, calculated and profit-driven with DDoS ransom being one of the nastiest elements.
dangerous, calculated and profit-driven with DDoS ransom being one of the nastiest elements. website traffic is not human, but bots. Bots are essentially software programs that perform automated, repetitive, pre-defined tasks. These tasks can include almost any interaction with software that has an Application Program Interface
website traffic is not human, but bots. Bots are essentially software programs that perform automated, repetitive, pre-defined tasks. These tasks can include almost any interaction with software that has an Application Program Interface 
 occurrence every year. Moreover, they are becoming harder to thwart because the attacks are allocated across sundry public anonymous proxies including
occurrence every year. Moreover, they are becoming harder to thwart because the attacks are allocated across sundry public anonymous proxies including 
 Anniversary. I suggested that we hire a professional photographer for this ‘once in a lifetime moment.’ However, weeks after the pictures were promised, all attempts to make contact were avoided. Finally, I tracked the photographer down and demanded the photos. He broke down and blurted out that ‘ransomware had encrypted his computer which was filled with years of work. He followed the instructions, but his files were deleted.’ I had to ask if he had a backup, he just hung his head and said ‘he meant to get around to it….’
Anniversary. I suggested that we hire a professional photographer for this ‘once in a lifetime moment.’ However, weeks after the pictures were promised, all attempts to make contact were avoided. Finally, I tracked the photographer down and demanded the photos. He broke down and blurted out that ‘ransomware had encrypted his computer which was filled with years of work. He followed the instructions, but his files were deleted.’ I had to ask if he had a backup, he just hung his head and said ‘he meant to get around to it….’ wearable devices and encrypts the victims’ data making it inaccessible until the victim pays for a decryption key.
wearable devices and encrypts the victims’ data making it inaccessible until the victim pays for a decryption key. 
 C-Suite executives. This group has access to sensitive employee, and/or customer data, banking, and/or securities accounts. Phishers target this group with e-mails and web-pages embedded with malicious code. When e-mail attachments are opened, or web-pages clicked the code is activated. The malicious code unleashes backdoors, remote access or embeds keyloggers; and within hours or days, the phisher gains access.
C-Suite executives. This group has access to sensitive employee, and/or customer data, banking, and/or securities accounts. Phishers target this group with e-mails and web-pages embedded with malicious code. When e-mail attachments are opened, or web-pages clicked the code is activated. The malicious code unleashes backdoors, remote access or embeds keyloggers; and within hours or days, the phisher gains access. Informational footprints that individuals, corporations, organizations and governments leave behind on the WWW or other open source tools, contains incredibly useful information. This information is often referred to as OSINT, and it is helpful because it can reveal actions and/or intent; and ultimately can give the holder of this information the upper hand or edge over your competition or target.
Informational footprints that individuals, corporations, organizations and governments leave behind on the WWW or other open source tools, contains incredibly useful information. This information is often referred to as OSINT, and it is helpful because it can reveal actions and/or intent; and ultimately can give the holder of this information the upper hand or edge over your competition or target.







 most profitable elements-mobile payments to insurance. Industry analysts estimate that traditional financial services industries could be at risk of being lost to standalone FinTech companies within 5 years.Additionally, FinTech is making an impact on the industry tripling to more than $9+ billion in the US in 2014 alone. (Economist.com)
most profitable elements-mobile payments to insurance. Industry analysts estimate that traditional financial services industries could be at risk of being lost to standalone FinTech companies within 5 years.Additionally, FinTech is making an impact on the industry tripling to more than $9+ billion in the US in 2014 alone. (Economist.com) Information security principally means ‘data security’ and at the core of information security efforts is the CIA triad-Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. The CIA triad is comprised of the objectives needed to achieve its sole purpose of safeguarding data from unauthorized access, disclosure, modification, inspection, recording or destruction of data. Infomation security coverage includes both electronic and paper.
Information security principally means ‘data security’ and at the core of information security efforts is the CIA triad-Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. The CIA triad is comprised of the objectives needed to achieve its sole purpose of safeguarding data from unauthorized access, disclosure, modification, inspection, recording or destruction of data. Infomation security coverage includes both electronic and paper. Security’ with respect to the protection of any digital data. Additionally, CyberSecurity protects the integrity of computing assets belonging to or connecting to a network; with its sole purpose to defend all assets against all threat actors throughout the entire life cycle of a cyber attack.
Security’ with respect to the protection of any digital data. Additionally, CyberSecurity protects the integrity of computing assets belonging to or connecting to a network; with its sole purpose to defend all assets against all threat actors throughout the entire life cycle of a cyber attack.
 as Social Engineering. Social engineers are ruthless and innovative criminals who take advantage of human behavior to gain access to data, networks or infiltrate businesses; because it is often ‘easier to exploit an individual’s penchant to trust than discovering new methods to hack’ your systems.
as Social Engineering. Social engineers are ruthless and innovative criminals who take advantage of human behavior to gain access to data, networks or infiltrate businesses; because it is often ‘easier to exploit an individual’s penchant to trust than discovering new methods to hack’ your systems.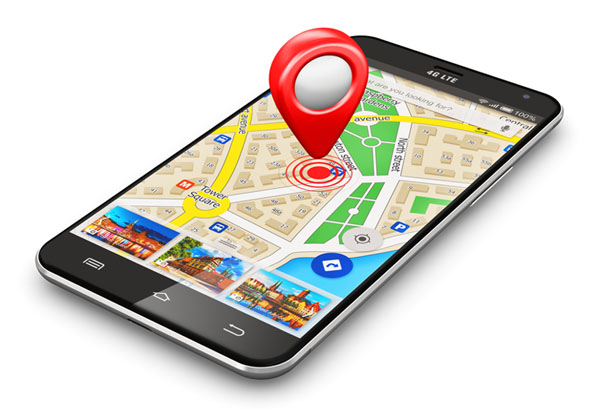
 You enter a sender’s social networking username (Creepy works with Twitter and Flickr) hit the ‘Geolocate button’ and Creepy collects all the geographical information available on the platforms, via photos that the sender has shared online. The end result being a navigable embedded Google map with latitude and longitude, date and time and what is more disturbing, often the text that accompanied the location/photo-For an additional personal effect.
You enter a sender’s social networking username (Creepy works with Twitter and Flickr) hit the ‘Geolocate button’ and Creepy collects all the geographical information available on the platforms, via photos that the sender has shared online. The end result being a navigable embedded Google map with latitude and longitude, date and time and what is more disturbing, often the text that accompanied the location/photo-For an additional personal effect. However, as we have seen from above, individuals need to be careful about the information we share with the millions of people on the internet. The majority of individuals do not realize that geotagging is active either because default enables it or disabling it is not showing as an option. Users need to think wisely next time they opt-in for geolocation features by clicking “allow” or “this application wants to use your current location” dialog box on your smartphone or tablet.
However, as we have seen from above, individuals need to be careful about the information we share with the millions of people on the internet. The majority of individuals do not realize that geotagging is active either because default enables it or disabling it is not showing as an option. Users need to think wisely next time they opt-in for geolocation features by clicking “allow” or “this application wants to use your current location” dialog box on your smartphone or tablet.