Last month my 97-year-old Grandparents were celebrating their 70th Wedding  Anniversary. I suggested that we hire a professional photographer for this ‘once in a lifetime moment.’ However, weeks after the pictures were promised, all attempts to make contact were avoided. Finally, I tracked the photographer down and demanded the photos. He broke down and blurted out that ‘ransomware had encrypted his computer which was filled with years of work. He followed the instructions, but his files were deleted.’ I had to ask if he had a backup, he just hung his head and said ‘he meant to get around to it….’
Anniversary. I suggested that we hire a professional photographer for this ‘once in a lifetime moment.’ However, weeks after the pictures were promised, all attempts to make contact were avoided. Finally, I tracked the photographer down and demanded the photos. He broke down and blurted out that ‘ransomware had encrypted his computer which was filled with years of work. He followed the instructions, but his files were deleted.’ I had to ask if he had a backup, he just hung his head and said ‘he meant to get around to it….’
Ransomware is malware which installs covertly on a victim’s computer, smartphone or  wearable devices and encrypts the victims’ data making it inaccessible until the victim pays for a decryption key. IOT/Ransomware
wearable devices and encrypts the victims’ data making it inaccessible until the victim pays for a decryption key. IOT/Ransomware
Ransomware will target and encrypt all files on the targeted network. Additionally, if online backups are located, more often than not, they may also be encrypted or deleted in order to prevent the organization from recovering encrypted data without first making the ransom payment.
Once the encryption process is complete, the splash screen appears, explaining that your data has been encrypted, time restriction threats, and specific payment amount usually in the form of a cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin. Bitcoin is preferred by cybercriminals because it is an encrypted, completely anonymous payment system independent from any central bank.
Before a payment can even be made, a cryptocurrency wallet must be attained. The wallet is principally a sequence of letters and numbers used as a private encryption key.
Each cryptocurrency wallet varies from each other including the diverse mediums the wallets are stored on; or as in the case of a hybrid, offering more than one method of accessing the wallet.
The wallet types include Mobile which is run on a smartphone application; Online which is a web-based wallet on either a real or virtual server; Hybrid which encrypts the private data before being sent to the online server. Hardware is dedicated hardware that stores the user’s private keys securely-USB devices for transport and security.
The one similarity among all the wallets is, if you lose your private encryption key, then you lose your money.

Once uniquely a consumer threat, ransomware’s technical capabilities paired with exceptional social engineering strategies have evolved into an efficient global business model and a ‘cash cow’ for cybercriminals. The same can not be said for the targeted organizations’ bottom line. Either directly or indirectly, ransomware can have a treacherous effect including productivity losses; reputational loss and substantial legal fines.
Furthermore, attacks that include the theft of regulated data comprised of personally identifiable information (PII), sensitive health information and/or credit card data are particularly sinister because of the probable data breach notification requirements, leading to potentially hefty regulatory penalties; financial loss and/or failure particularly since the average cost of a data breach is currently tracking at $4+ million per breach and expected to rise.
 Cybercriminals will often leverage vulnerabilities in operating systems and software in order to gain initial access; However, the most successful attacks occur when cybercriminals exploit the organization’s own employees. Targeted social engineering techniques will ultimately do the ‘dirty work’ of infecting networks and operating systems, as employees remain the weakest link from a security perspective.
Cybercriminals will often leverage vulnerabilities in operating systems and software in order to gain initial access; However, the most successful attacks occur when cybercriminals exploit the organization’s own employees. Targeted social engineering techniques will ultimately do the ‘dirty work’ of infecting networks and operating systems, as employees remain the weakest link from a security perspective.
The Enemy (Only a fractional list)
CryptoWall 3.0
CryptoWall 3.0 is extensively distributed using various exploit kits, spam campaigns, and malvertising techniques. It uses I2P anonymity network proxies for communicating command and control servers (C&C); TOR network for payments using Bitcoin.
CryptoWall 3.0, uses an AES key for file encryption. For added confusion, the AES key is encrypted further using a unique public key generated on the server making it completely impossible to find the actual key needed to decrypt the files.
CTB-Locker or Curve-Tor-Bitcoin Locker.
Curve based on elliptic curves, which encrypts the affected files with a unique RSA key; Tor from the malicious server placed in The Onion Router (TOR) domain; Bitcoin refers to Bitcoin payments.
CTB-Locker uses RSA-2048 Encryption. It is widespread through the use of spoofed UPS Notifications with attachments, usually a Microsoft Office document. Attempts to view will ‘require enabling macros.’ Once the macros are enabled, encryption of your files ensues.
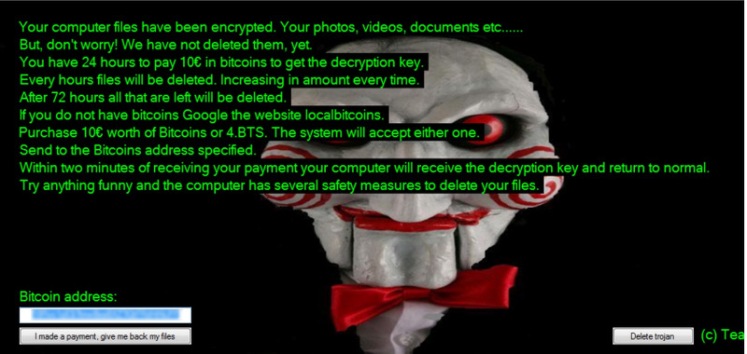
Jigsaw
Trend Micro in 2016 discovered the crypto-ransomware called Jigsaw, aptly named after the horror movie Saw. However, although it was removed from one site, it is believed within the cybercommunity that Jigsaw can be still downloaded from other locations.
Jigsaw is different from other crypto-ransomware because it not only ‘locks users out from accessing their files, but Jigsaw will actually delete them.’ Initially, the program creates a copy of the user’s files, and encrypts them into ‘.fun,’ ‘.kkk,’ ‘.gws,’ and ‘.btc,’ files and deletes the original file. There is an animated 60-minute timer, which adds strain and anxiety due to the snowball effect of the deletion of files hourly.
Worse yet, there is never just one variant of any crypto-ransomware programs, as the cybercriminals evolve so does their destructive programs. In the earlier versions of Jigsaw, the average ransom requested was ‘$150 in Bitcoin,’ but in recent variants, the ransom request is upwards of ‘$5000 in Bitcoin and appends the user’s files in .epic.’
Why is crypto-ransomware a nightmare for end-users?
- The encryption is unbreakable.
- It will encrypt all files–Documents, images, photos, music, and videos.
- It can cause additional stress and confusion by scrambling file names and/or appends the files with different extensions.
- Even if you pay the ransom, there is no guarantee that your data will be released and there is an even greater chance you will become a victim again.
- The estimated cost of ransomware globally is in the $Billions with no end in sight.
Why is ransomware so pervasive?
- The human factor. It is easier to get an individual to open an attachment through the use of social engineering tactics than it is to break into a network.
- One of the more insidious threats that can be downloaded through phishing e-mails are RATs or Remote Access Trojans. What makes them different is the program provides the ability to spy on their targets. RATs not only collect keystrokes, usernames, passwords, screenshots, browser history, Social Security Numbers, and e-mails. They install backdoors allowing the cybercriminal unencumbered access. Thus allowing the cybercriminal to monitor user behavior, copy files, access other connected systems and utilize the targets internet connection for other illegal activity.
- Estimates indicate that more than 90% of US organizations have no form of social engineering training for their employees. This makes it incredibly easy for cybercriminals and opens the organizations up to enormous risk including financial and reputational.
- Reports estimate that more than 70% of successful data breaches started with a Phishing attack.
- Approximations indicate that as many as 70 million phishing e-mails are sent out daily, and upwards of 7 out of 10 are infected with ransomware.
- Smaller businesses and municipalities are often unprepared to deal with advanced cyberattacks like ransomware and/or have a casual bring your own device policy (BYOD) that can leave them vulnerable to exploits.
- Lack of online safety awareness makes individuals prone to manipulation by other social engineering attacks, opening an opportunity for the cybercriminal to gain access and launch attacks from the inside.
- Public institutions and government agencies which have critical databases often use outdated software and equipment, which means that their computer networks are chockfull with security holes just begging to be exploited.
Most common methods used to spread ransomware:
- Ransomware as a Service (RaaS). Allows just about anyone with or without IT or coding experience, to become a successful cybercriminal at minimal expense.
- Phishing e-mail campaigns embedded with malicious code.
- Aggressive spam campaigns that spoof fax messages-UPS, ADP, AMEX, etc.
- Pop-Ups.
- SMS messages.
- Drive-by downloads.
- Drive-by downloads happen when you land on a compromised web page,i.e., injected with malicious code. The user will either be directed to another webpage which hosts an exploit kit or is prompted with an alert box you have to click on to ignore.
- Internet traffic that redirects to malicious sites (Pharming).
- Pharming can be completed either by changing the host’s file on the victim’s computer or by exploiting a vulnerability in a DNS server software.
Protecting yourself and your organization requires action.
- Never open e-mails from unknown senders.
- Never download attachments or click on links from unknown senders.
- Never click on pop-ups.
- Never insert an unknown USB stick into your PC, Laptop, etc.
- Never store sensitive or critical data only on your PC. Have at least two backups– an external hard drive and in the cloud.
- Never leave your password on a sticky post where an intruder can find it.
- Adjust your browsers’ security and privacy settings.
- Use an HTTPS connection for all credit card transactions.
- Keep your operating system and software up to date.
- Never log in as an administrator. Rather choose a guest with limited privileges.
- Removed outdated plugins and add-ons.
- Disable ActiveX content in Microsoft Office applications.
- Block TOR and I2P.
- Disable remote desktop.
- Use an anti-virus product.
- Use a traffic filtering solution that can provide proactive anti-ransomware protection.
- Block binaries running from %APPDATA% and %TEMP% paths.
- Work with the C-Suite to enact social engineering awareness training for all employees.
- Consider a Computer Incident Response Team (CIRT), based on the organization’s needs and available sources.
- Have a tested business continuity plan in the event of any cyberattack.
Cybersecurity is a shared responsibility. Stop. Think. Connect.